In the ever-evolving world of SEO, staying updated with Google’s algorithm changes and ranking factors is crucial for maintaining and improving your website’s visibility. One of the significant updates in recent times revolves around Core Web Vitals (CWV) and Google Page Experience ranking factors.
What are Core Web Vitals?
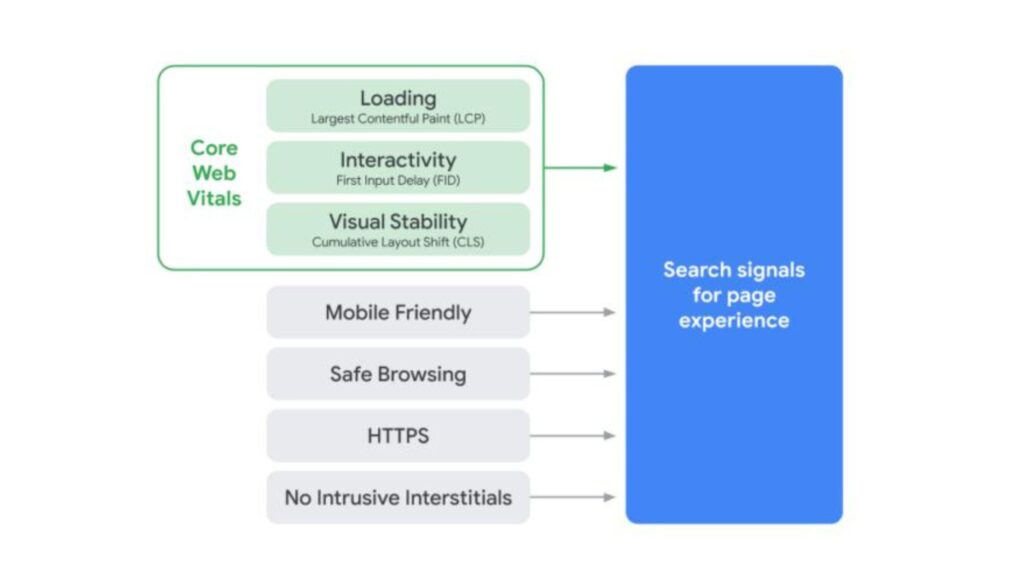
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific factors that Google considers critical in a webpage’s overall user experience. They are part of Google’s larger set of Web Vitals, which measure aspects of web page performance. The three main components of CWV are:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page first starts loading.
First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. Pages should have an FID of less than 100 milliseconds to ensure users can interact with the content without noticeable delays.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Pages should maintain a CLS of less than 0.1, ensuring that elements on the page are stable and do not shift unexpectedly as the page loads.
Google Page Experience Update

Google’s Page Experience update integrates Core Web Vitals with other existing ranking signals, aiming to provide a holistic view of a website’s user experience. The update includes the following factors:
Mobile-friendliness: Ensures that a website is optimized for mobile devices.
Safe-browsing: Checks that the website is free from malicious content or malware.
HTTPS: Ensures the website uses a secure connection.
No intrusive interstitials: Ensures that content is easily accessible to users without intrusive pop-ups.
Importance of CWV and Page Experience
The integration of CWV into Google’s ranking algorithm signifies the growing importance of user experience in SEO. Websites that prioritize user experience are likely to perform better in search rankings. With the Page Experience update, Google aims to reward sites that not only provide relevant content but also offer a smooth, secure, and pleasant browsing experience.
How to Optimize for CWV and Page Experience?

Improve Loading Times (LCP)
Optimize Images: Compress and resize images to reduce loading times.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute content across various servers to speed up delivery.
Minimize CSS and JavaScript: Reduce file sizes and remove unnecessary code to improve load times.
Enhance Interactivity (FID)
Reduce JavaScript Execution Time: Minimize the time it takes for the browser to execute JavaScript.
Optimize Web Workers: Use web workers to run scripts in the background, reducing the load on the main thread.
Defer Unused JavaScript: Load only the necessary JavaScript during the initial load and defer the rest.
Ensure Visual Stability (CLS)
Set Size Attributes for Media: Specify width and height attributes for images and videos to prevent layout shifts.
Reserve Space for Ads: Allocate space for ads to avoid unexpected shifts when ads load.
Avoid Inserting Content Above Existing Content: Prevent layout shifts by not inserting new content above existing content.
Other Page Experience Factors
Mobile Optimization: Ensure your website is responsive and works well on all mobile devices.
Security: Implement HTTPS to secure your website and protect user data.
User-Friendly Design: Avoid intrusive interstitials and pop-ups that hinder user experience.



